Android Error Inflating Class: Complete Guide to Troubleshooting

Encountering the “Error Inflating Class” message on an Android device or during app development can be both confusing and frustrating. This error often appears suddenly, crashes your app on launch, and leaves you staring at a wall of red text in Logcat. If you’ve ever wondered what it really means, why it happens, and how to fix it for good, you’re in the right place.
This in‑depth guide is designed to help Android developers and technically inclined users understand the root causes of the “Error Inflating Class” issue and walk through practical, reliable solutions. By the end of this article, you’ll not only know how to resolve the error when it appears, but also how to prevent it from creeping back into your projects.
Who This Guide Is For
This article is especially useful if you:
- Are an Android developer encountering this error during app development
- Are debugging a crashing app that fails to inflate a layout
- Have basic knowledge of Android app development and XML layouts
- Use Android Studio and Logcat for debugging
To follow along comfortably, you should have access to a development environment and a basic understanding of how Android layouts and views work.
What Is the “Error Inflating Class” in Android?
In Android, layouts are typically defined using XML files. When your app runs, the Android framework reads these XML files and “inflates” them—that is, it converts each XML tag into a corresponding View object in memory.
The “Error Inflating Class” occurs when Android fails to create (instantiate) one of these view classes. When this happens, the app usually crashes immediately, often during startup or when navigating to a specific screen.
In simple terms: Android tried to load a view from your XML layout, but something went wrong, so it gave up.
What You’ll Need
Before diving into troubleshooting, make sure you have the following:
- A computer with Android Studio installed
- Access to an Android device or emulator
- The latest Android SDK (or a compatible version for your project)
- Basic knowledge of XML layouts and Android development concepts
- Familiarity with Logcat for reading error messages
Understanding Why the Error Happens
The “Error Inflating Class” message is not a single error—it’s a symptom. It usually wraps around a more specific exception that points to the real problem. Common underlying causes include:
- Typos or incorrect class names in XML layout files
- Referencing a custom view class incorrectly
- Using XML attributes that are not supported by the view
- Missing constructors in custom view classes
- Incompatible or outdated libraries
- Mismatched Android SDK versions
Because the error is generic, Logcat is your best friend when it comes to identifying the exact cause.
How to Identify the Cause of the Error
Follow these steps to pinpoint the issue:
1. Open Android Studio and launch your project.
2. Ensure your project is fully synced with the latest Gradle files.
3. Run your application in debug mode to reproduce the crash.
4. Open Logcat in Android Studio.
5. Look for the red error message containing “Error inflating class”.
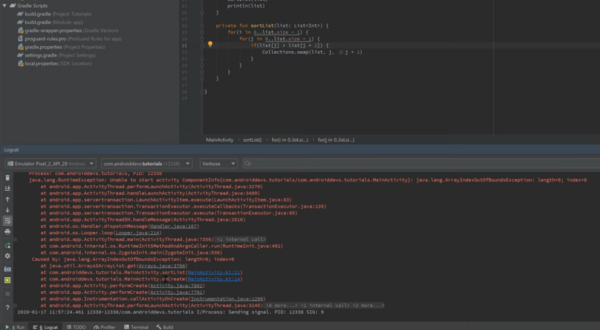
6. Carefully read the lines above and below it—these often mention:
- The specific view class that failed
- The XML layout file involved
- The exact line number in the layout
This information is crucial. The first error in the stack trace is usually the most important one.
How to Resolve the “Error Inflating Class” Issue
Once you’ve identified the problematic area, try the following solutions.
1. Check Your XML Layout File
- Look for typos in view names and attributes
- Ensure all view tags match valid Android classes
- Verify that custom views use the correct fully qualified class name
This is often the fastest fix, especially for simple layouts.
2. Verify Custom View Classes
If you’re using a custom view:
- Make sure the class exists in your project
- Ensure it extends a valid Android view (e.g., View, TextView, LinearLayout)
- Confirm that required constructors are implemented
- Check that the package name in XML matches the actual class path
3. Review XML Attributes
Using unsupported or incorrect attributes can cause inflation to fail.
- Double‑check attribute names and values
- Ensure attributes are compatible with the view type
- Remove recently added attributes to isolate the issue
4. Update SDK and Libraries
Outdated or incompatible dependencies can trigger inflation errors.
- Update the Android SDK
- Upgrade third‑party libraries to compatible versions
- Ensure your compileSdkVersion, minSdkVersion, and targetSdkVersion are properly aligned
5. Rebuild and Rerun the Project
After making changes:
- Clean and rebuild your project
- Run the app again to confirm the error is resolved
Tips and Best Practices
To reduce the chances of encountering this error in the future:
- Regularly update your Android SDK and dependencies
- Use clear, consistent naming conventions for views and IDs
- Rely on version control to track changes and roll back errors quickly
- Take advantage of Android Studio tools like Layout Inspector
- Be cautious when copying XML snippets from external sources
- Test your app on multiple devices and Android versions
- Document your layouts and custom views for easier maintenance
Common Issues and Their Solutions
- Problem: Error caused by outdated library references. Solution: Update all dependencies to their latest compatible versions.
- Problem: Custom view class not found. Solution: Verify the class path, package name, and ensure the class exists and is imported correctly.
- Problem: Incorrect XML attribute usage. Solution: Cross‑check attributes against the official Android documentation.
- Problem: Incompatible Android version. Solution: Review your app’s minSdkVersion and ensure it matches your target devices.
Ensuring a Smooth Android Development Experience
The “Error Inflating Class” issue can feel intimidating at first, but it becomes much easier to manage once you understand what’s happening behind the scenes. A systematic approach—checking XML layouts, reviewing Logcat output, and validating custom views—will solve most cases quickly.
By applying the best practices outlined in this guide and staying up to date with Android development tools and libraries, you’ll not only fix this error when it appears but also build more stable, reliable Android applications in the long run.ractices. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you should be able to eliminate this error and improve the reliability of your Android applications. Continuing to refine your development practices and staying informed of the latest Android updates will further enhance your development experience.
It indicates that the framework is unable to create an instance of a view class specified in your XML layout.
Use Android Studio’s Logcat to identify the specific class causing the error and check your XML for inconsistencies.
Common reasons include typos in XML, outdated libraries, or incorrect class paths for custom views.
Yes, keeping your SDK and libraries up to date ensures compatibility and can resolve many related issues.
Adopting best practices such as regular updates, thorough testing, and proper documentation can help prevent this error.






User forum
0 messages