Understand Unique Cooling System featured in Galaxy S7
3 min. read
Published on
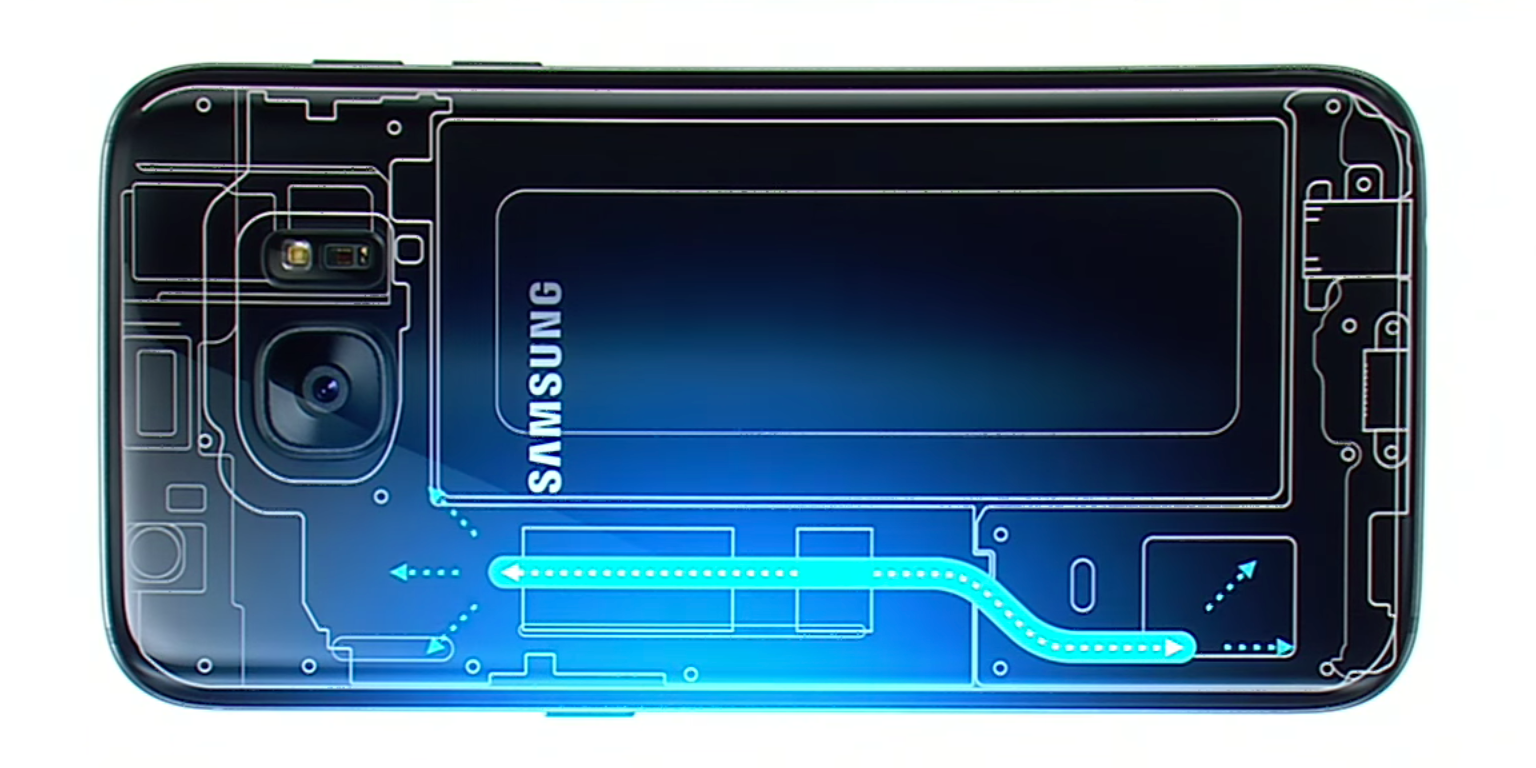
You might recall that Samsung presented a new cooling system for the Galaxy S7 at this year’s MWC conference, but I bet that you paid much more attention to the shiny device than to such technical details. Now, that the handset is in your pocket, things have changed and it is in your favor to understand this unique Cooling System featured in Galaxy S7. After all, this system ensures that your handset can run faster than ever without overheating. You know that this is essential as long as making calls and running intensive apps and games can make the processor and RAM work much harder, and this leads to only one thing: increased heat generation and more problems.
That is why I have decided to closely investigate how such a cooling system really works and if it is as efficient as the Korean company claims and wants us all to believe. You know that manufacturers try to create new different systems to counteract heat and this includes cooling systems, or even processor throttling. This is no different for the Galaxy S7, but things are taken to a new level as long as the water is the one truly used as a coolant.
Water in a smartphone might sound rather crazy at first – I know that too, but the truth is that this is much more easier than it sounds. The cooling systems the Galaxy S7 is somehow similar to those used in PCs. Many PC manufacturers use water as a coolant to avoid extreme heat, just as it happens in car engines. Even though you see the similarity of the concept, there are some major differences in how Android smartphone cooling systems work when compared to the ones of a PC.
That is why Samsung decided to release a detailed interview with their engineers who designed this cooling system to help us understand more. They are clear about the fact that the unique heat pipe featured in the flagship series is the thinnest in the world, with 0.4mm in diameter and 0.2mm in width.
Unlike any conventional thermal spread sheet technology, the thermal spreader that they are telling us about uses changes in the phases of water to radiate heat. It has a porous structure on the inside where water absorbs heat, turns into steam and then, it moves through pipes. After losing the heat, the steam liquefies, and turns back into water in the structure. This cycle can successfully dispel heat and as I have said it before, the entire process happens inside that small space that of no more than 0.2mm wide.
Pretty interesting, don’t you think? Let me know what you think of it in the comments area from below. And just in case things don’t go as planned for your handset and this cooling system still fails to do its job, you can read and apply the steps from this guide: How to Solve Galaxy S7 Overheating Issues.









User forum
0 messages